The Tattooed Body in Japan Tells the Story of an Evolution
In this book, journalist Philippe Pons examines the turbulent history of tattooing and its decline in Japanese society.
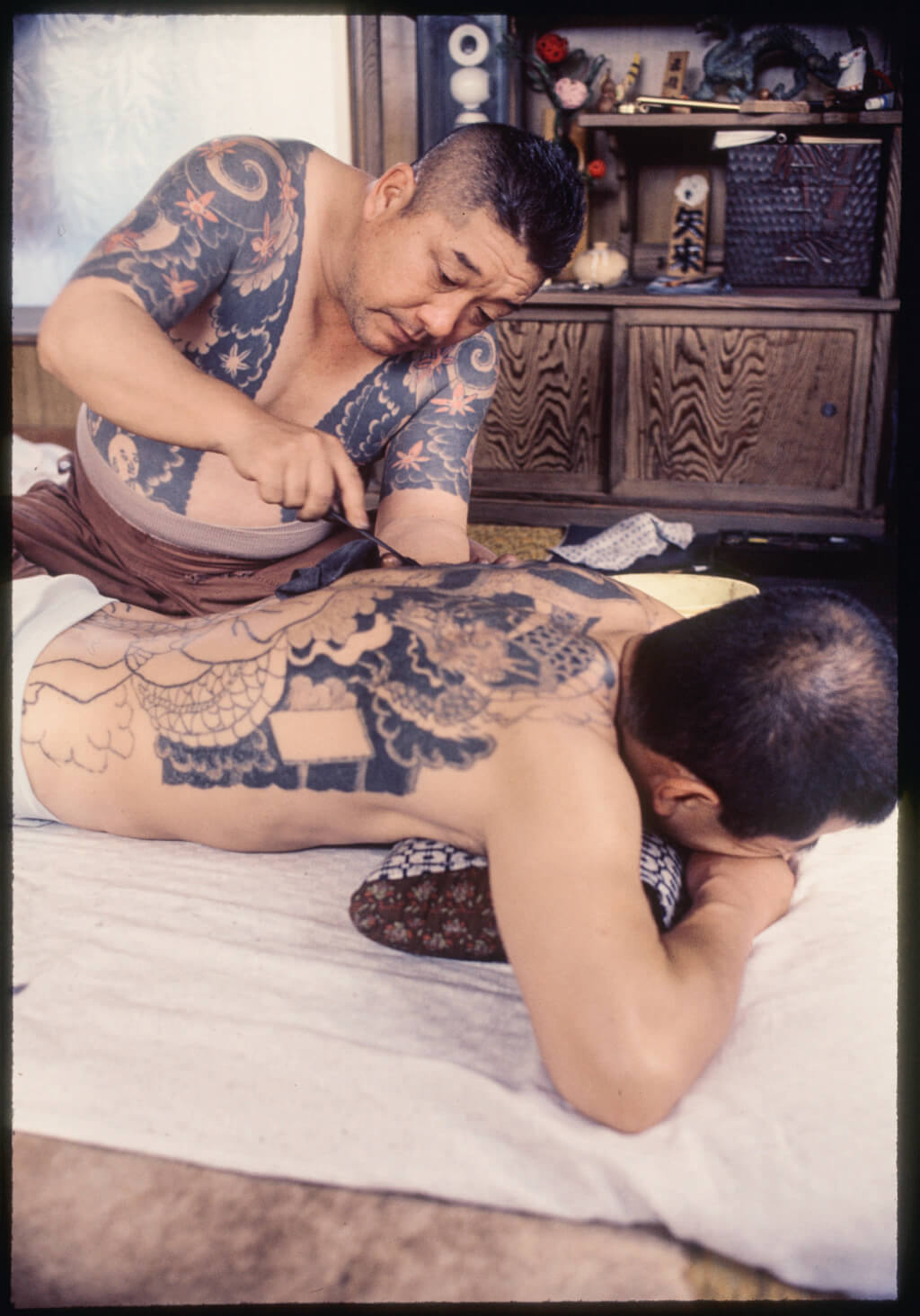
HORIBUN II, one of the most famous tattoo masters during the second half of the 20th century. Photo © Ian Buruma
Tattooing has a meaning, and it evolves. Over time, the place and significance this art holds in Japanese society have changed. The book Le corps tatoué au Japon, estampes sur la peau (‘The Tattooed Body in Japan: Engravings on the Skin’), released in 2018 by journalist Philippe Pons, examines tattooing from a historical, anthropological, and aesthetic perspective.
In this book, Philippe Pons, Japan correspondent for Le Monde, compiles interviews conducted over three decades with tattoo masters along with his research and analysis.
A change of meaning
After they were banned by the emperor during the Meiji period (1867-1912), tattoos were appropriated by the yakuza. It was only in 1948, when the country was under American occupation, that General MacArthur lifted the ban. In the collective imagination, however, tattoos remain linked to gangs and the rejection of the system.
Philippe Pons thinks that the younger generations are now distorting traditional tattoo art, which is connected to engraving. As Gilles Fumey stresses in the newspaper Libération, the art of tattooing ‘lives on thanks to a small, semi-clandestine community of enthusiasts who are steadily increasing in number: there were two hundred and fifty tattoo artists in 1980, three thousand in 2017. Strangely, however, it feels as though a decline is likely…’
The book places this popular art in Japan’s social history. In the 17th century, ‘brocaded skin’, with the entire surface of the body covered with tattoos, was popular with Japanese people, whereas nowadays, young people prefer more discreet tattoos (wan pointo tatu). Philippe Pons examines this surprising evolution as, since the beginning of the 21st century, the great art of traditional Japanese tattooing, appreciated and revered overseas, has been on the wane in Japan and is losing its meaning and authenticity.
This book follows on from Peau de brocart. Le corps tatoué au Japon (‘Brocaded Skin: The Tattooed Body in Japan’), published in 2000 by Seuil.
Le corps tatoué au Japon, estampes sur la peau (‘The Tattooed Body in Japan: Engravings on the Skin’) (2018), a book by Philippe Pons, is published by Gallimard (not currently available in English).
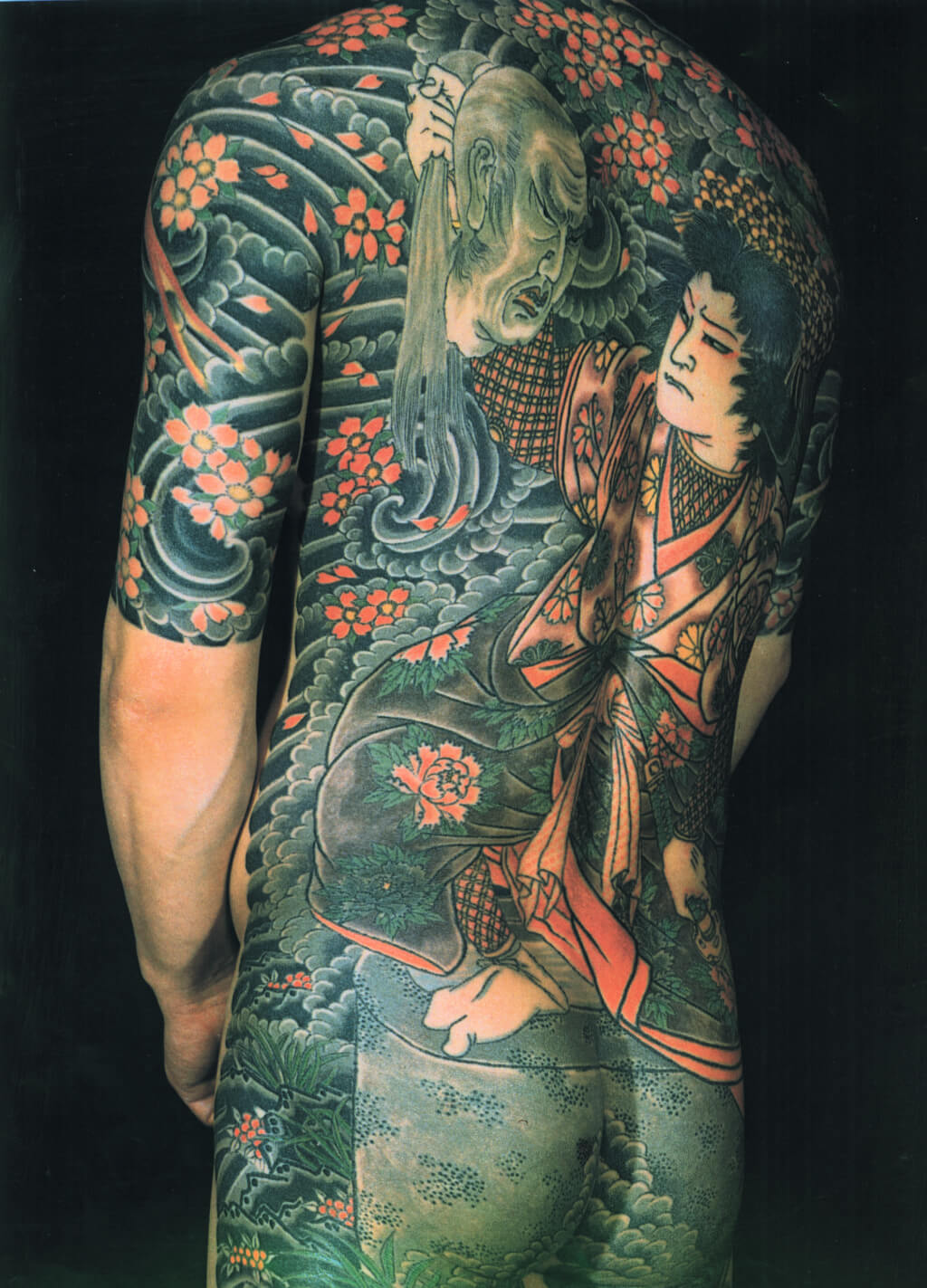

This tattoo by HORIYOSHI II depicts the warrior Inusaka Keno identifying the decapitated head of his enemy. Photo © Keibunsha Co. Ltd., Tokyo

© Gallimard
TRENDING
-
A House from the Taisho Era Reveals Its Secrets
While visiting an abandoned building, Hamish Campbell discovered photographs the owner had taken of the place in the 1920s.

-
The Taboo-Breaking Erotica of Toshio Saeki
The master of the 1970s Japanese avant-garde reimagined his most iconic artworks for a limited box set with silkscreen artist Fumie Taniyama.

-
With Meisa Fujishiro, Tokyo's Nudes Stand Tall
In the series 'Sketches of Tokyo', the photographer revisits the genre by bringing it face to face with the capital's architecture.

-
Masahisa Fukase's Family Portraits
In his series ‘Family’, the photographer compiles surprising photos in which he questions death, the inescapable.

-
Hajime Sorayama's Futuristic Eroticism
The illustrator is the pioneer for a form of hyperrealism that combines sensuality and technology and depicts sexualised robots.





